 Database replication involves creating and maintaining multiple copies of the same database for recovery and backup purposes. It requires transferring files from one computer or server to another so that all users share the same data. This results in a distributed database that gives users access to necessary information without interfering with others’ work. Normalization, which eliminates ambiguous data and inconsistent files among users, serves as the primary motivation for database replication. A distributed database management system (DDBMS) guarantees that anything that is added, deleted, or adapted on one server is reflected automatically in all other locations, creating an overall consistent database.
Database replication involves creating and maintaining multiple copies of the same database for recovery and backup purposes. It requires transferring files from one computer or server to another so that all users share the same data. This results in a distributed database that gives users access to necessary information without interfering with others’ work. Normalization, which eliminates ambiguous data and inconsistent files among users, serves as the primary motivation for database replication. A distributed database management system (DDBMS) guarantees that anything that is added, deleted, or adapted on one server is reflected automatically in all other locations, creating an overall consistent database.
Database replication can be performed in three different ways:
- Snapshot replication: Data is copied from one server to another. (Read our blog post about snapshot recovery here.)
- Merging replication: Data from multiple databases is combined into a single database.
- Transactional replication: Users receive full initial copies of the database and then receive periodic updates as data changes.
The most common method of database replication is multi-master replication, which allows data to be updated by any user and stored on a group of computers. The alternative to this process, multi-slave replication, gives sole responsibility to a master computer that makes changes whenever a user updates data. Multi-master replication allows for a quicker and more efficient way to replicate data. Replication occurs through database transaction capturing, which obtains changes made to the database synchronously, asynchronously, or both, depending on the method of capture.
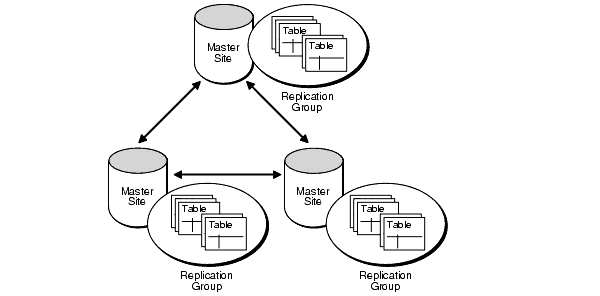
All of the various types and methods of database replication can make it complicated to implement, especially when data increases in size and magnitude. A pro/con list should indicate whether the database replication is worth the trouble.
Pros
- Database replication allows all system users to easily and efficiently share data. It recognizes data modifications and copies the information so that it can be accessed.
- During multi-master replication if one master fails, another one can continue to update.
- Multi-master replication allows masters to be located across several physical sites and distributed across an entire network.
- Multi-master replication is very powerful and flexible.
- It is possible to create multiple replication groups within a single database.
- Database replication turns out to be complicated when data increases in size and magnitude.
- Conflict resolution can become increasingly complex due to the number of nodes involved in multi-master replication.
- Asynchronous replication, associated with multi-master replication, increases the possibility for inconsistent data changes, or “conflicts” to occur during database transaction capturing.
- Setting push jobs using asynchronous replication to run at very short intervals can use up an excessive amount of system resources.
Data replication serves as an incredibly powerful and functional solution to data backup systems. However, it is not an easily managed solution, and comes with a great deal of complexity. It is recommended that multi-master replication be used to protect a critical database in case the primary site becomes unavailable due to system or network outages. For applications that require multiple access points for users, data replication can help distribute a heavy load and provide continuous availability for located data. Alternative backup needs can be accommodated by other backup systems. Read more about backup solutions.
Sources
