The Cloud – What it is…. What it does… Should I get it?
 Cloud computing, by definition, refers to the on-demand delivery of IT resources and applications via the internet with a pay-as-you-go pricing model. There are many reasons why businesses are investing in the cloud, some of the reasons are financially motivated, while others address technical concerns.
Cloud computing, by definition, refers to the on-demand delivery of IT resources and applications via the internet with a pay-as-you-go pricing model. There are many reasons why businesses are investing in the cloud, some of the reasons are financially motivated, while others address technical concerns.
Whether you are running applications that share photos to millions of mobile users or you are supporting the critical operations of your business, the cloud provides rapid access to flexible and low cost IT resources. With cloud computing, you don’t need to make large upfront investments in hardware and spend a lot of time on the heavy lifting of managing that hardware. Instead, you can provision exactly the right type and size of computing resources you need to power your newest and brightest ideas, or operate your IT department.
How it Works
Cloud Computing provides a simple way to access servers, storage, databases and applications over the Internet. Cloud Computing providers such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft own and maintain the network connected hardware required for these application services, while you provision and use what you need via a web application.
Virtual Servers
A virtual server can be a private server or a public server, and is a method of server hosting, using virtual machines. The virtual part simply means that it is not a dedicated server – that is the entire computer is not dedicated to running the server software. It is comprised of a computer and various server programs that is located at your (Private) office or someone else’s location (Public). Some Internet service providers offer a virtual server service instead of or in addition to virtual hosting. Using a virtual server, a company or individual with a web site can not only have their own domain name and IP address, but can administer their own file directories, add e-mail accounts and address assignments, assign multiple domain names that resolve to a basic domain name without involvement from the ISP, manage their own logs and statics analysis and maintain passwords. Users of a virtual server, however, do not have to manage the hardware aspects of running a server and effectively share the cost of expensive line connections to the internet.
How Virtual Servers Work
 Server computers -- machines that host files and applications on computer networks -- have to be powerful. Some have central processing units (CPUs) with multiple processors that give these servers the ability to run complex tasks with ease. Computer network administrators usually dedicate each server to a specific application or task. Many of these tasks don't play well with others -- each needs its own dedicated machine. One application per server also makes it easier to track down problems as they arise. It's a simple way to streamline a computer network from a technical standpoint.
Server computers -- machines that host files and applications on computer networks -- have to be powerful. Some have central processing units (CPUs) with multiple processors that give these servers the ability to run complex tasks with ease. Computer network administrators usually dedicate each server to a specific application or task. Many of these tasks don't play well with others -- each needs its own dedicated machine. One application per server also makes it easier to track down problems as they arise. It's a simple way to streamline a computer network from a technical standpoint.
There are a couple of problems with this approach, though. One is that it doesn't take advantage of modern server computers' processing power. Most servers use only a small fraction of their overall processing capabilities. Another problem is that as a computer network gets larger and more complex, the servers begin to take up a lot of physical space. A data center might become overcrowded with racks of servers consuming a lot of power and generating heat.
Server virtualization attempts to address both of these issues in one fell swoop. By using specially designed software, an administrator can convert one physical server into multiple virtual machines. Each virtual server acts like a unique physical device, capable of running its own operating system (OS). In theory, you could create enough virtual servers to use all of a machine's processing power, though in practice that's not always the best idea.
Virtualization isn't a new concept. Computer scientists have been creating virtual machines on supercomputers for decades. But it's only been a few years since virtualization has become feasible for servers. In the world of information technology (IT), server virtualization is a hot topic. It's still a young technology and several companies offer different approaches.1
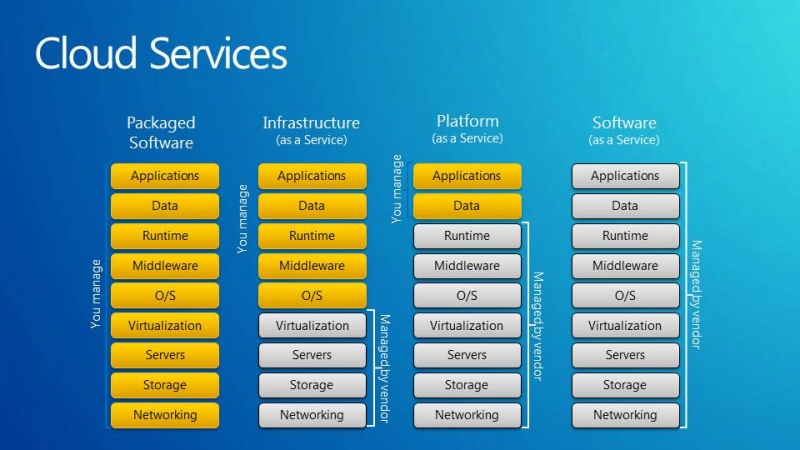
Cloud Computing Models - (Anything)aaS
Cloud computing is providing developers and IT departments with the ability to focus on what matters most and avoid identical work like procurement, maintenance and capacity planning. As cloud computing has grown in popularity, several different models and deployment strategies have emerged to help meet specific needs of different users. Each type of cloud service, and deployment method, provides you with different levels of control, flexibility and management. Understanding the differences between IaaS, PaaS and SaaS as well as what deployment methods you can use will help you decide what types of services are right for you.
- SaaS - Software as a Service – Software distribution model in which applications are hosted by a vendor or service provider and made available to customers over a network, typically the internet
- DaaS – Data as a Service is a cousin of SaaS. Like all members of the “as a Service” family, DaaS is based on the concept that the product, date in this case, can be provided on demand to the user regardless of geographic or organizational separation of provider and consumer. Additionally, the emergence of service-oriented architecture (SOA) has rendered the actual platform on which the data resides also irrelevant.
- DRaaS – Disaster Recovery as a Service – is the replication and hosting of physical or virtual servers by a third party to provide failover in the event of a man-made or natural disaster. DRaas can be especially useful for small to mid-size businesses that lack the necessary expertise to provision, configure and test an effective disaster recovery plan. Using DRaaS also means the organization doesn’t have to invest in and maintain their own off-side disaster recovery environment. An additional benefit is that DRaaS contracts can be flexible as the business’ needs change.
- IaaS – Infrastructure as a Services – A Type of cloud computing in which a third-party provider hosts virtualized computing resources over the internet
- MBaaS – Mobile Backend as a Service – also known as “Backend as a service” (Baas) is a model for providing web and mobile application developers with a way to link their applications to backend cloud storage and APIs exposed by back end applications while also providing features such as user management, push notifications and integration with social networking services. These services are provided via the use of custom software development kits (SDKs) and application programming interfaces (APIs). BaaS is a relatively recent development in cloud computing with most BaaS startups dating from 2011 or later.
- PaaS – Platform as a Service – is a category of cloud computing services that provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run and manage web applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with development and launching an application. PaaS can be delivered in two ways: as a public cloud service from a provider, where the consumer controls software deployment and configuration setting sand the provider provides the networks, servers, storage and another services to host the consumer’s application; or as software installed in private data centers or public infrastructure as a service and managed by internal IT departments.
- SECaas – Security as a service, is a business model which a large service provider integrates their security services into a corporate infrastructure on a subscription basis more cost effectively than most individuals or corporation can provide on their own, when total cost of ownership is considered. In this scenario, security is delivered as a service from the cloud, without requiring on-premises hardware avoiding substantial capital outlays. These security services often include authentication, anti-virus, anti-malware/spyware, intrusion detection and security event management, among others.
- ITaaS - IT as a Service - The entire process of IT management changes from maintaining software based products to integrating cloud based software, such as CRM and procurement solutions. For a business this integration changes the cost structure from maintaining legacy systems with large upfront costs to paying monthly for the Technology services the businesses need.
 So should you get in or on the Cloud?
So should you get in or on the Cloud?
The cloud can provide users with a number of different benefits. Many business both large and small use cloud computing today either directly through Google, Amazon or Microsoft or indirectly through Twitter, Facebook, Instagram instead of traditional on-site alternatives Here are a few reasons why cloud computing is so widely used among businesses today:
- Flexibility – Cloud computing allows users to switch applications easily and rapidly, using the one that suits their needs best. However, migrating data between applications can be time consuming. Emulation is now starting to come to forefront for migration. Emulation is the ability of a computer program to imitate another program or device.
- Reduction of Costs – unlike on-site hosting, the price of deploying applications in the cloud can be less due to lower hardware costs from more effective use of physical resources.
- Access from anywhere on anything – Whatever device you’re working on: PC, Mac, Tablet, Phone…Wherever you are: home, vacationing, in the office; Cloud computing allows employees to access business applications and work via the internet.
- The most up-to-date software - cloud providers upgrade software using the most up to date versions, service packs and antivirus and antispam software. Users no longer need to worry whether or not that are running the latest versions needed to run their applications. Or purchase newer versions of the software they are using. It is all part of the cloud package.
- Potential for greener and more economical – The average amount of energy needed for a computational action carried out in the cloud is far less than the average amount for an on-site deployment. This is because different organizations can share the same physical resources securely, leading to more efficient use of the share resources.
Resources:
1. http://computer.howstuffworks.com/
4. http://altis.com.au/business-intelligence-in-the-cloud/
5. http://www.cedar-rapids.org/